How to use layouts
This guide shows you how to use the Layout to arrange charts/components on the screen and customize the grid specifications.
The Page model accepts the layout argument, where you can input your Layout with a custom grid.
Use the default layout
The layout argument of the Page model is optional. If no layout is specified, all charts/components
will automatically be vertically stacked down the page in one column.
If that is your desired layout, you can create your charts/components without providing a Layout.
Default Layout
Configure the grid
To customize the grid arrangement, you can configure the grid parameter of the Layout model.
The example below shows how the grid works and how to specify a valid one:
- The
gridneeds to be provided asList[List[int]](for example,grid = [[0, 1], [0, 2]]) - The integers in the
gridcorrespond to the index of the chart/component inside the list ofcomponentsprovided toPage - The number of integers in the
gridneeds to match the number of chart/components provided - Each sub-list corresponds to a grid row (for example, row 1 =
[0, 1]and row 2 =[0, 2]) - Each element inside the sub-list corresponds to a grid column (for example, column 1 =
[0, 0]and column 2 =[1, 2]) - The integers in the
gridneed to be consecutive integers starting with 0 (for example,0,1,2) - Each chart/component will take the entire space of its grid area (empty spaces are currently not enabled)
- The area spanned by a chart/component in the grid must be rectangular
- The grid can be arbitrarily large, allowing arbitrarily granular control of the grid:
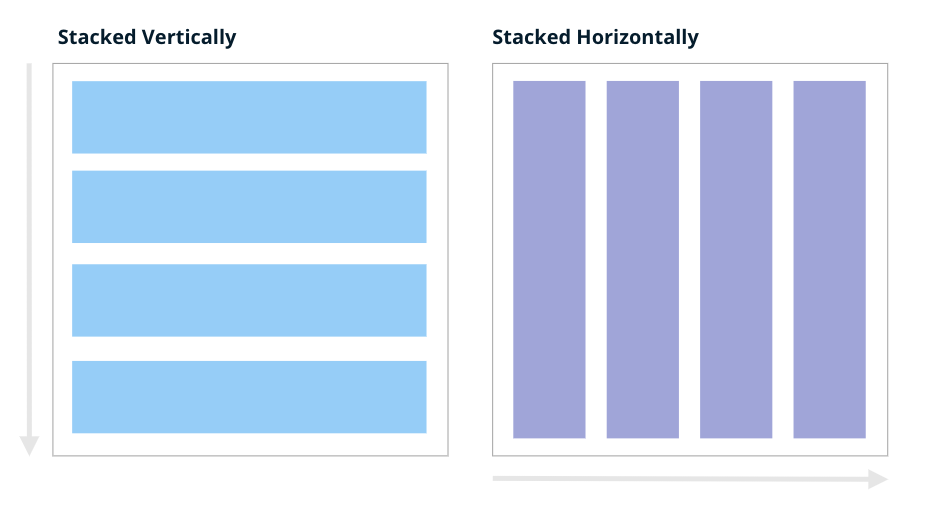
Stack components
- When no
Layoutis specified, components will automatically be stacked vertically down the page in one column. For instance, if you have three components, the defaultLayout.gridwill begrid = [[0], [1], [2]]. This means three equally sized rows, each containing a component spanning the entire width. - To stack components horizontally, set the grid as
grid = [[0, 1, 2]]. This defines a single row that occupies the entire width and height, divided into three equal columns.
Grid - basic example
Grid Arrangement - Basic Example
import vizro.models as vm
from vizro import Vizro
page = vm.Page(
title="one_left_two_right",
layout=vm.Layout(grid=[[0, 1],
[0, 2]]),
components=[vm.Card(text="""# Component 0"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 1"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 2"""),
],
)
dashboard = vm.Dashboard(pages=[page])
Vizro().build(dashboard).run()
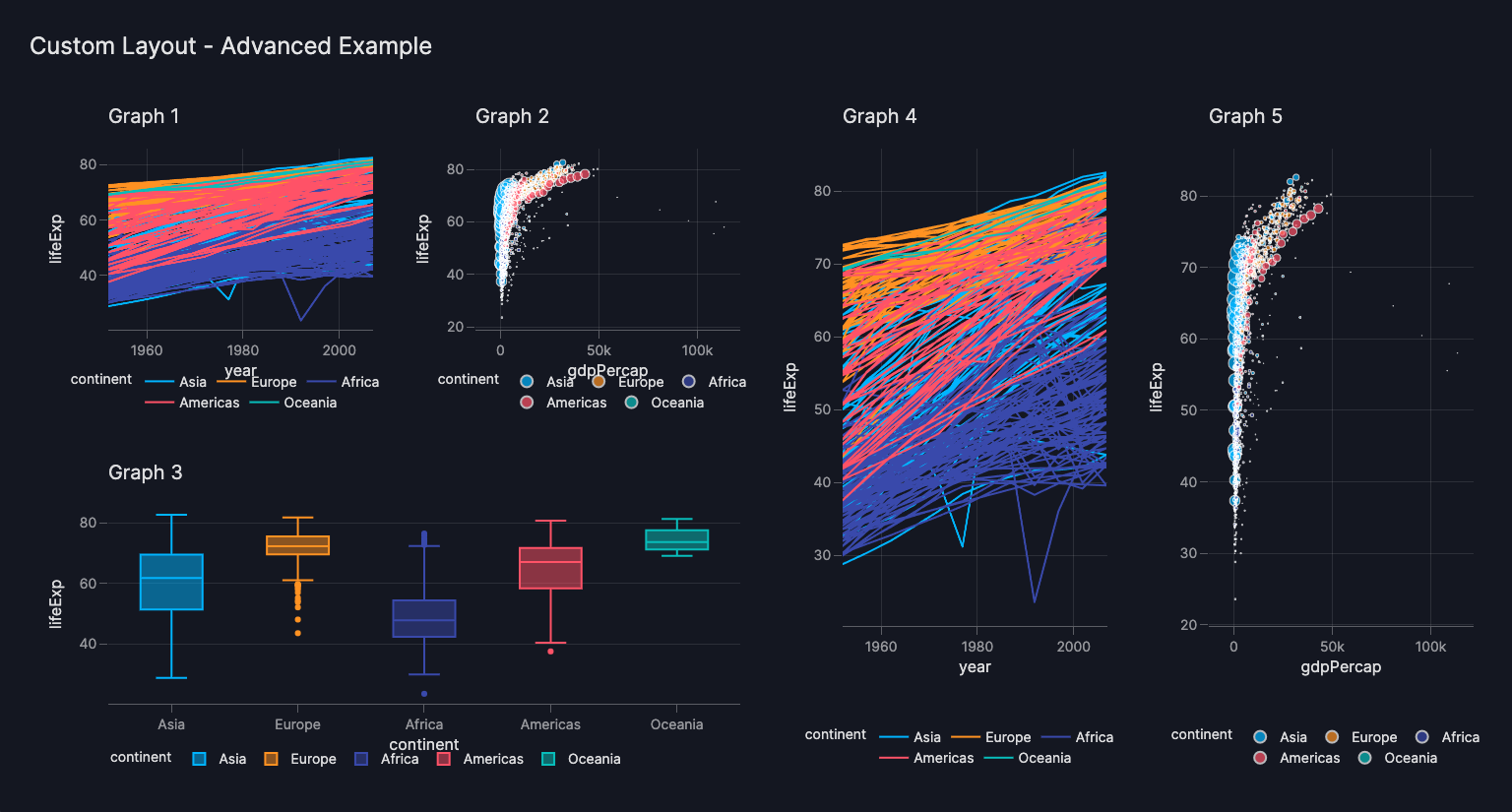
Grid - advanced example
The Layout provides full control over the arrangement of top-level components within a page,
allowing arbitrarily granular control of the grid by creating larger grids.
If you want to divide the grid into subgrids with finer control over these, you can use Containers.
See our section on when to use Containers vs. Page.layout for more information.
Grid Arrangement - Advanced Example
import vizro.models as vm
import vizro.plotly.express as px
from vizro import Vizro
gapminder = px.data.gapminder()
page = vm.Page(
title="Custom Layout - Advanced Example",
layout=vm.Layout(grid=[[0, 1, 3, 4],
[2, 2, 3, 4]]),
components=[
vm.Graph(
figure=px.line(
gapminder,
title="Graph 1",
x="year",
y="lifeExp",
color="continent",
),
),
vm.Graph(
figure=px.scatter(
gapminder,
title="Graph 2",
x="gdpPercap",
y="lifeExp",
size="pop",
color="continent",
),
),
vm.Graph(
figure=px.box(
gapminder,
title="Graph 3",
x="continent",
y="lifeExp",
color="continent",
),
),
vm.Graph(
figure=px.line(
gapminder,
title="Graph 4",
x="year",
y="lifeExp",
color="continent",
),
),
vm.Graph(
figure=px.scatter(
gapminder,
title="Graph 5",
x="gdpPercap",
y="lifeExp",
size="pop",
color="continent",
),
),
],
)
dashboard = vm.Dashboard(pages=[page])
Vizro().build(dashboard).run()
# Still requires a .py to add data to the data manager and parse YAML configuration
# See yaml_version example
pages:
- components:
- figure:
_target_: line
data_frame: gapminder
x: year
y: lifeExp
color: continent
title: Graph 1
type: graph
- figure:
_target_: scatter
data_frame: gapminder
x: gdpPercap
y: lifeExp
size: pop
color: continent
title: Graph 2
type: graph
- figure:
_target_: box
data_frame: gapminder
x: continent
y: lifeExp
color: continent
title: Graph 3
type: graph
- figure:
_target_: line
data_frame: gapminder
x: year
y: lifeExp
color: continent
title: Graph 4
type: graph
- figure:
_target_: scatter
data_frame: gapminder
x: gdpPercap
y: lifeExp
size: pop
color: continent
title: Graph 5
type: graph
layout:
grid: [[0, 1, 3, 4], [2, 2, 3, 4]]
title: Custom Layout - Advanced Example
Use custom layout examples
Below is a table of examples you can take as a reference to create some selected layouts:
| Configuration | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
layout=Layout(grid=[[0]]) or layout=None |
one_left | 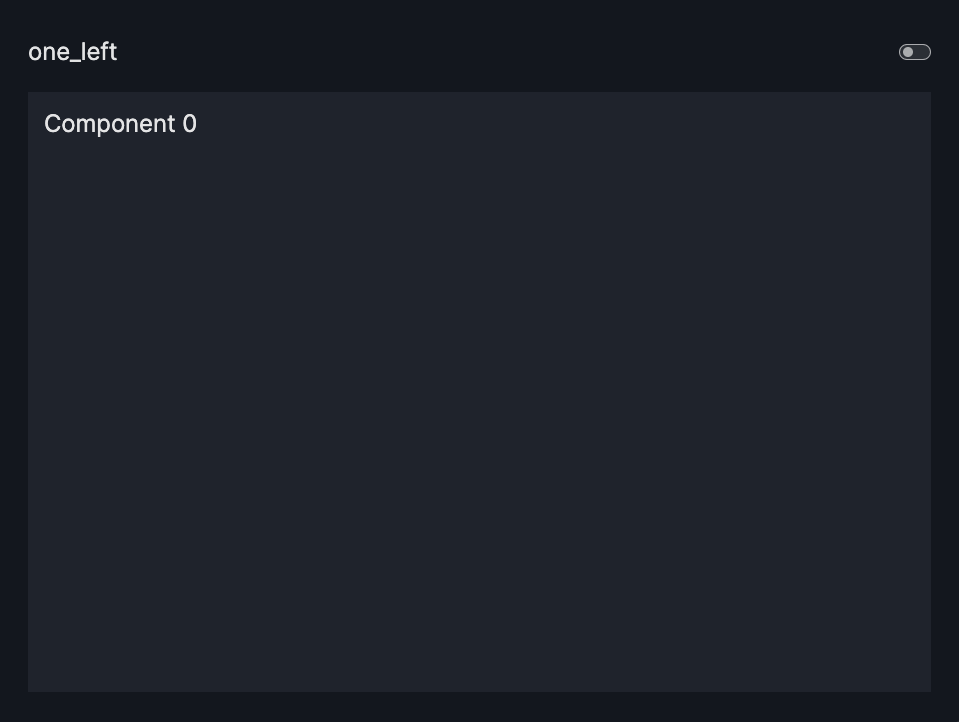 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0],[1]]) or layout=None |
two_left | 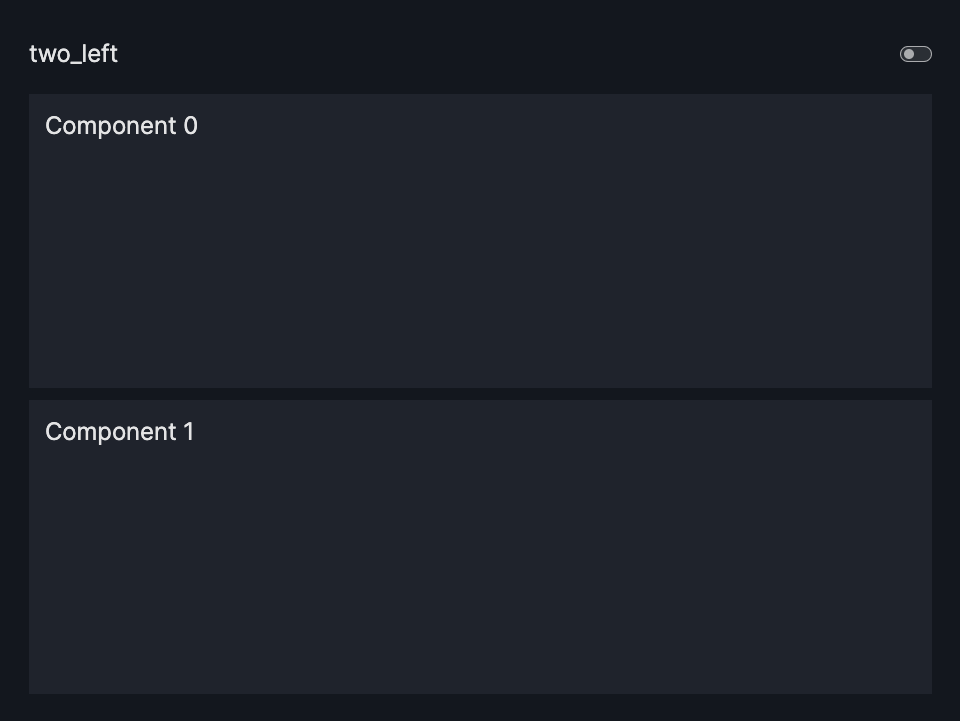 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1]]) |
two_top | 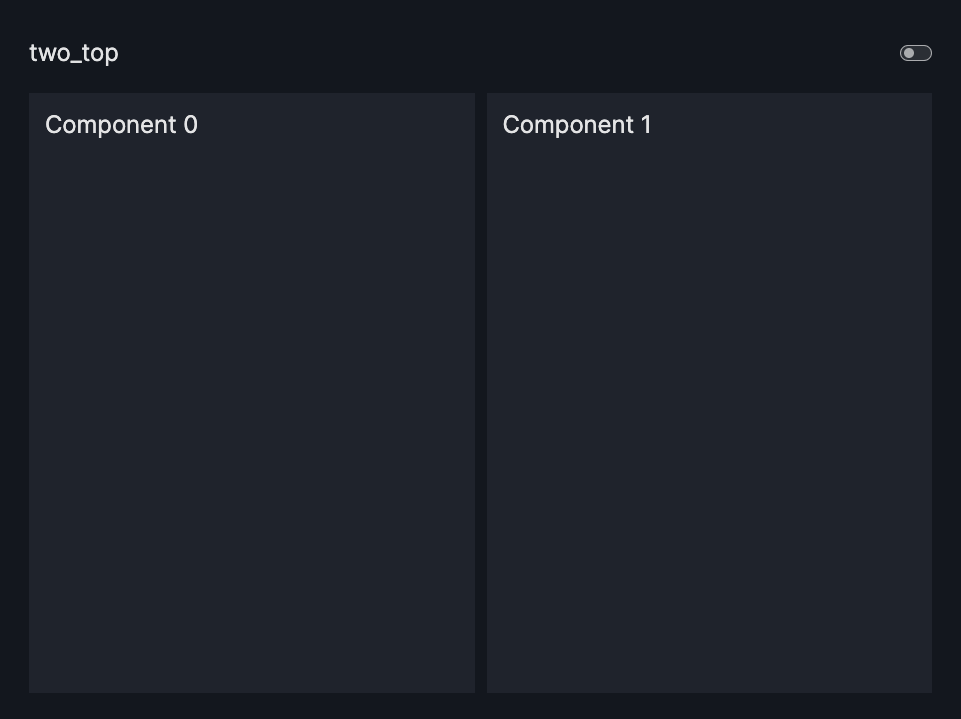 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0],[1],[2]]) or layout=None |
three_left | 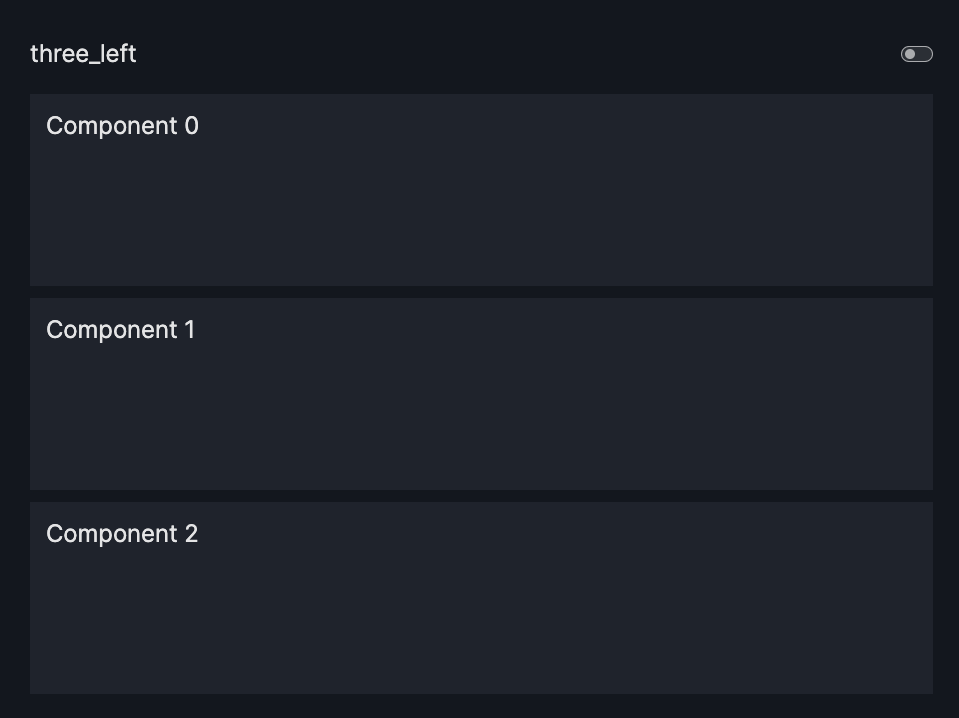 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1],[0,2]]) |
one_left_two_right | 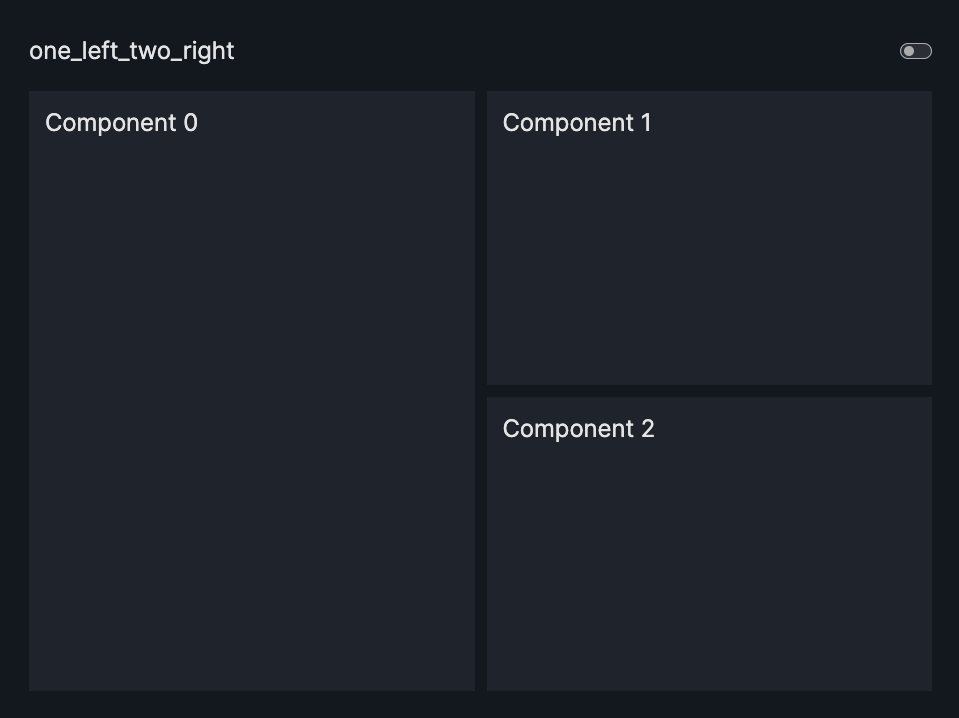 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,0],[1,2]]) |
one_top_two_bottom | 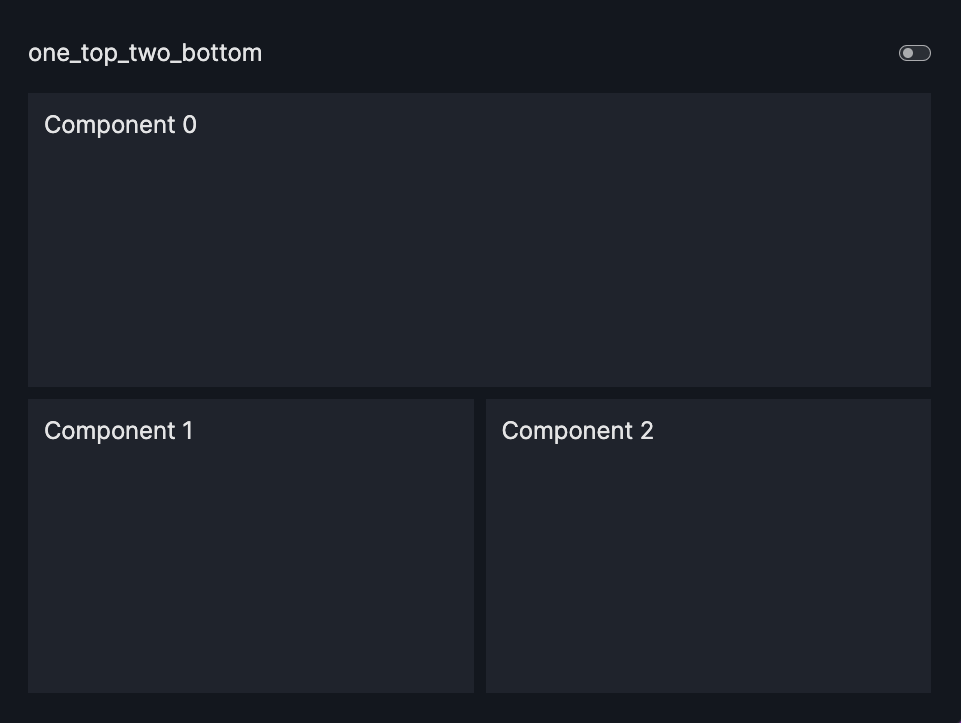 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1],[2,2]]) |
two_top_one_bottom | 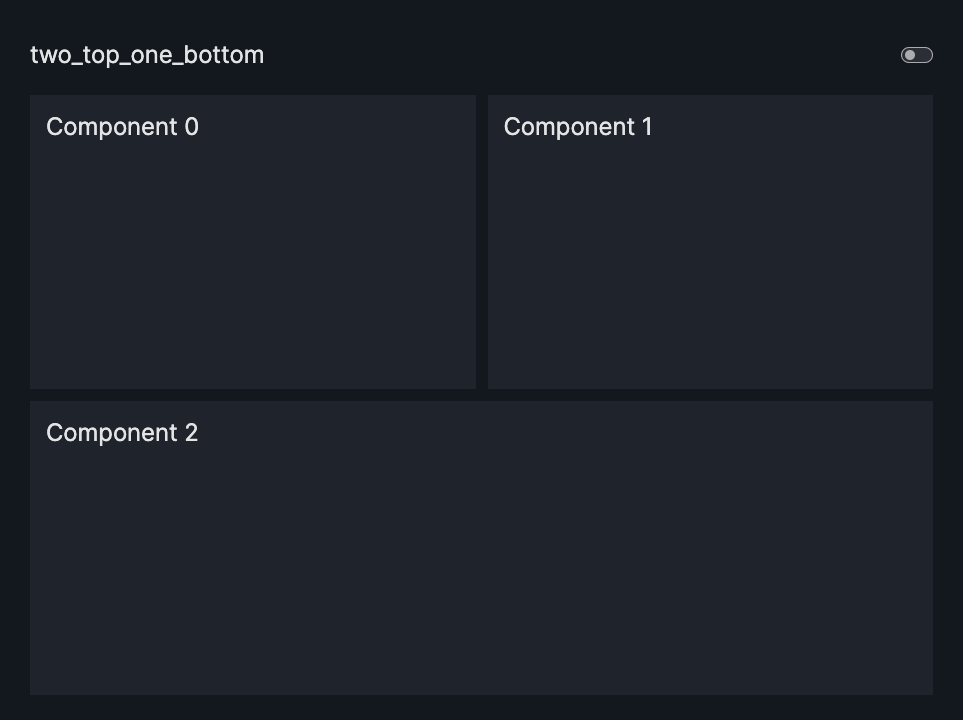 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]) |
one_left_three_right | 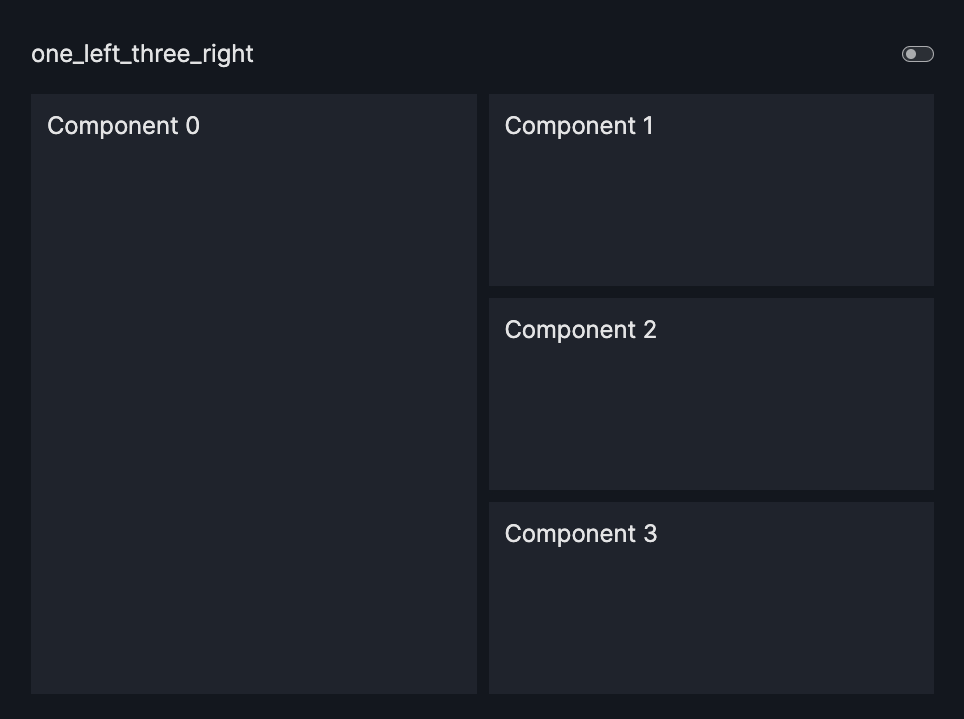 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1],[2,3]]) |
two_left_two_right | 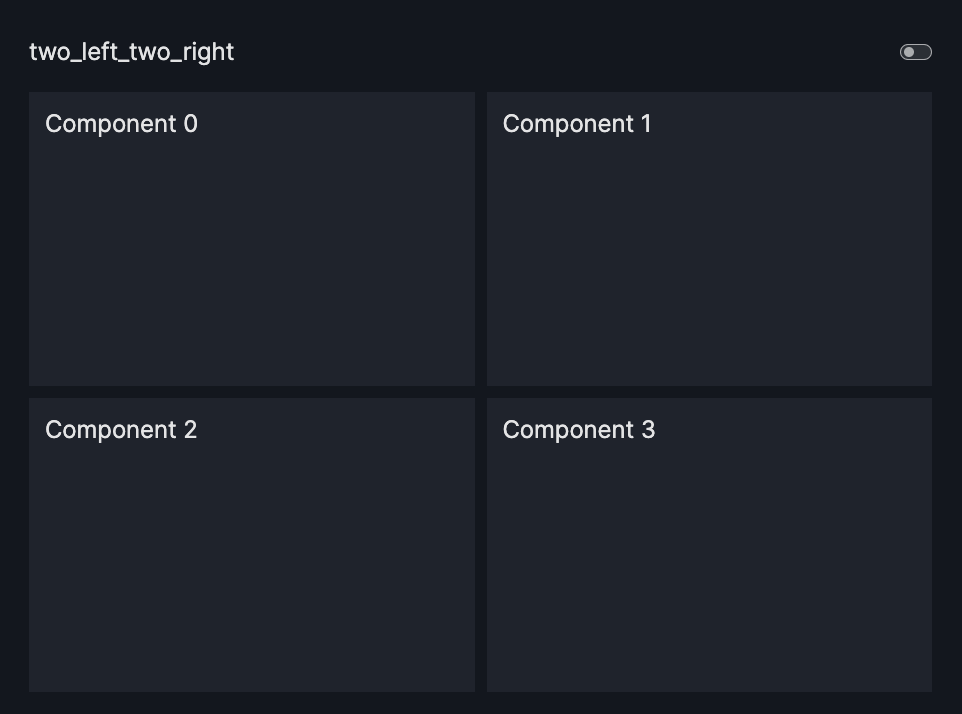 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,3],[1,3],[2,3]]) |
three_left_one_right | 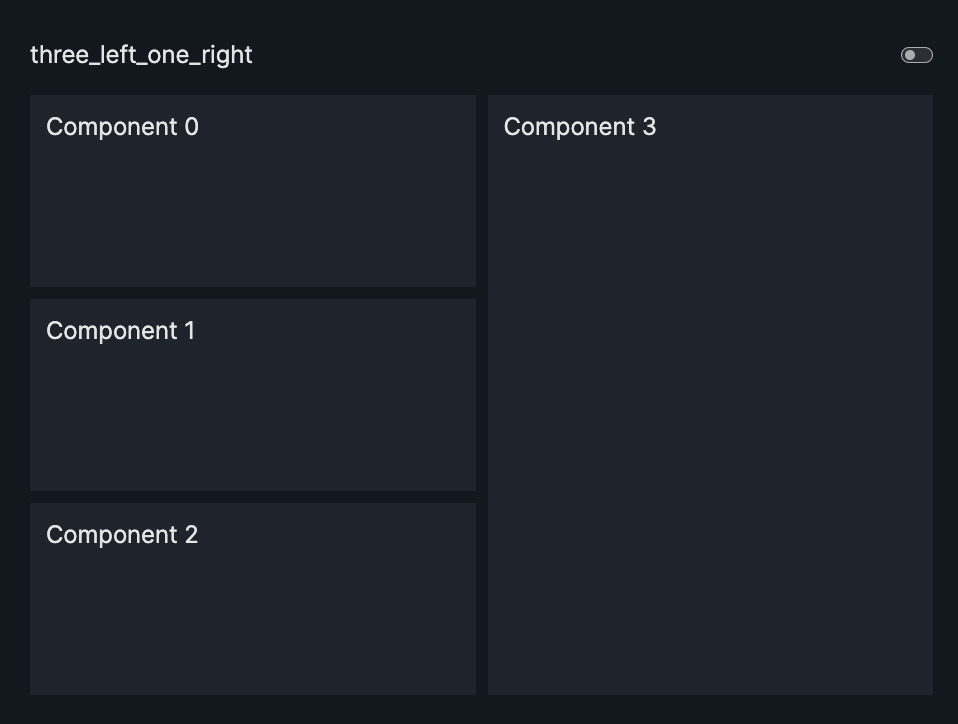 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,0,0],[1,2,3]]) |
one_top_three_bottom | 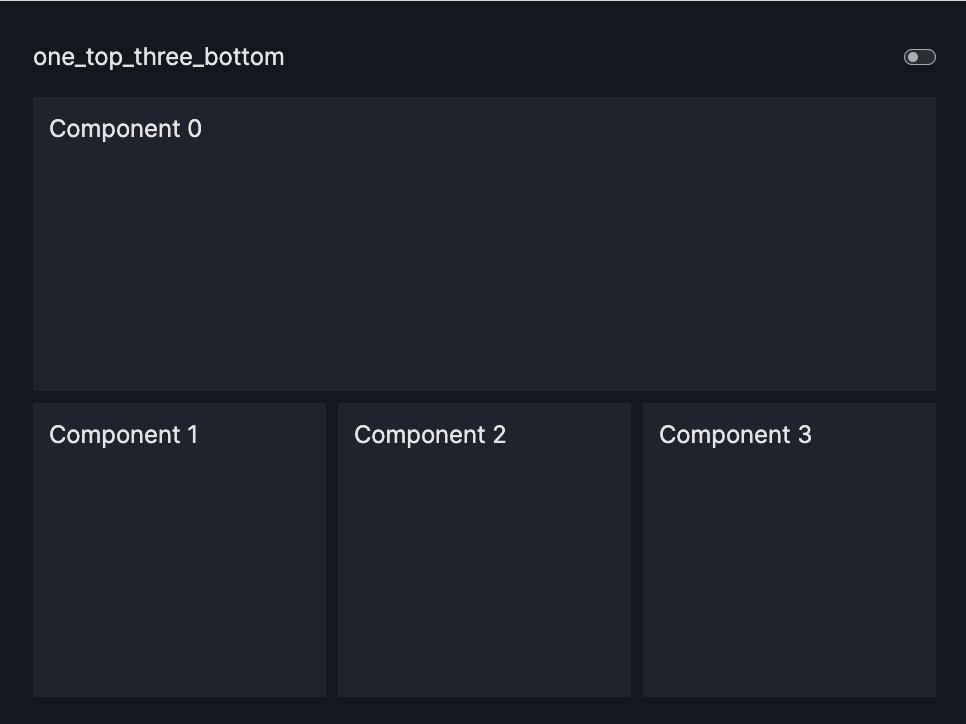 |
layout=Layout(grid=[[0,1,2],[3,3,3]]) |
three_top_one_bottom | 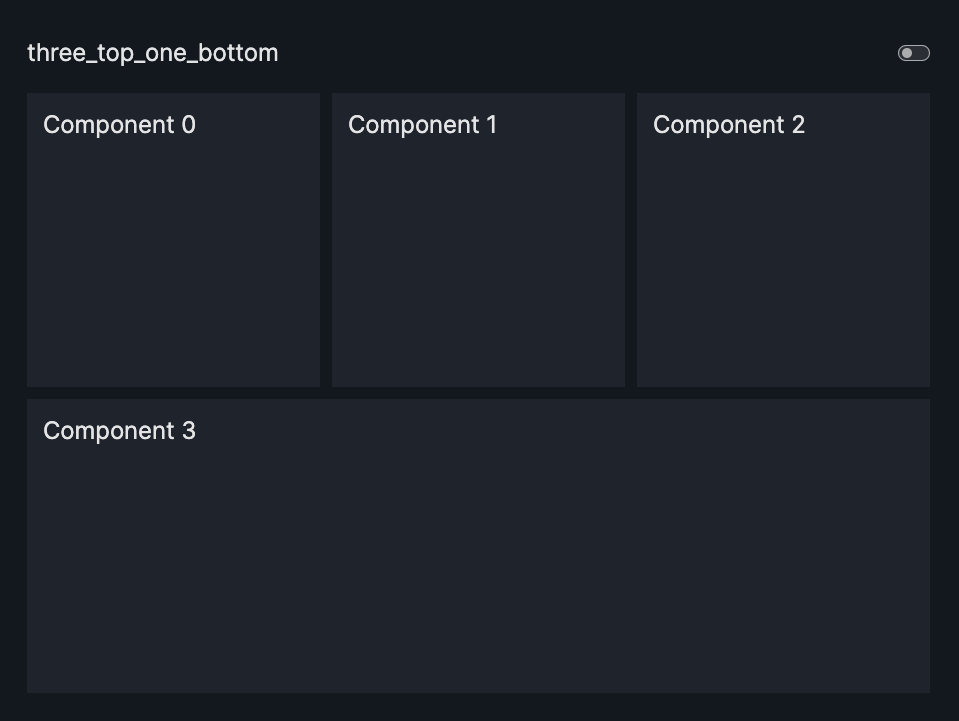 |
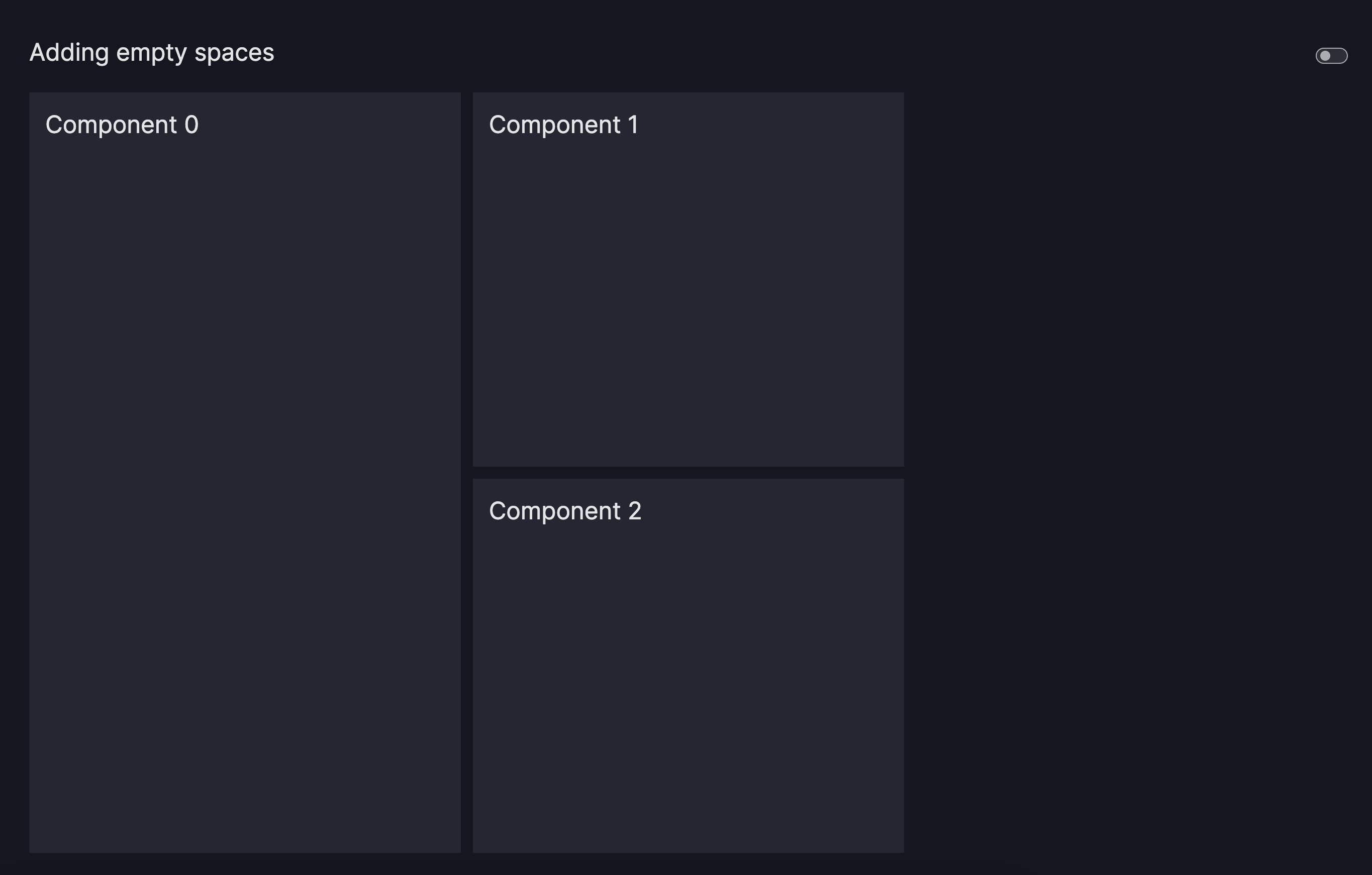
Add empty spaces to the grid
One approach to organize the dashboard's layout involves integrating empty spaces.
This can be achieved by specifying -1 within your grid layout.
Adding Empty Spaces
import vizro.models as vm
from vizro import Vizro
page = vm.Page(
title="Adding empty spaces",
layout=vm.Layout(grid=[[0, 1, -1],
[0, 2, -1]]),
components=[vm.Card(text="""# Component 0"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 1"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 2"""),
],
)
dashboard = vm.Dashboard(pages=[page])
Vizro().build(dashboard).run()
# Still requires a .py to add data to the data manager and parse YAML configuration
# See yaml_version example
pages:
- components:
- text: |
# Component 0
type: card
- text: |
# Component 1
type: card
- text: |
# Component 2
type: card
layout:
grid: [[0, 1, -1], [0, 2, -1]]
title: Adding empty spaces
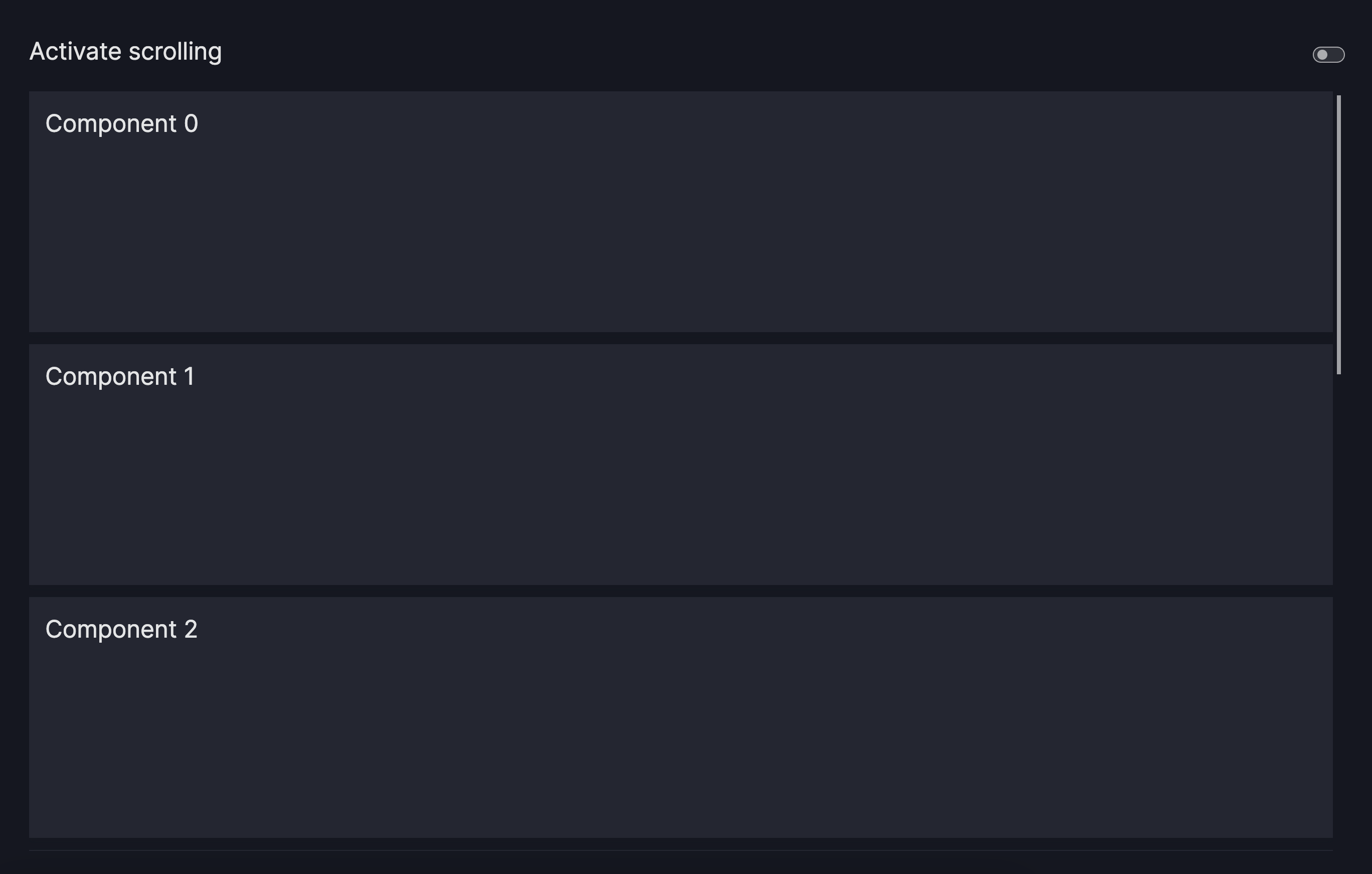
Control the scroll behavior
By default, the grid will try to fit all charts/components on the screen. This can lead to distortions of the chart/component looking squeezed in. You can control the scroll behavior of the grid by specifying the following:
row_min_height: Sets a chart/component's minimum height. Defaults to 0px.col_min_width: Sets a chart/component's minimum width. Defaults to 0px.
Activate Scrolling
import vizro.models as vm
from vizro import Vizro
page = vm.Page(
title="Activate scrolling",
layout=vm.Layout(grid=[[i] for i in range(8)],
row_min_height="240px"),
components=[vm.Card(text="""# Component 0"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 1"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 2"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 3"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 4"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 5"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 6"""),
vm.Card(text="""# Component 7"""),
],
)
dashboard = vm.Dashboard(pages=[page])
Vizro().build(dashboard).run()
# Still requires a .py to add data to the data manager and parse YAML configuration
# See yaml_version example
pages:
- components:
- text: |
# Component 0
type: card
- text: |
# Component 1
type: card
- text: |
# Component 2
type: card
- text: |
# Component 2
type: card
- text: |
# Component 4
type: card
- text: |
# Component 5
type: card
- text: |
# Component 6
type: card
- text: |
# Component 7
type: card
layout:
grid: [[0], [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7]]
row_min_height: 240px
title: Activate scrolling
Further customizations
For further customizations, such as changing the gap between row and column, refer to the
documentation of the Layout model.
Alternative layout approaches
In general, any arbitrarily granular layout can already be achieved using Page.layout alone and is our
recommended approach if you want to arrange components on a page with consistent row and/or column spacing.
Alternative layout approaches: Tabs and Containers
Tabs and Containers provide an alternative approach to customize your page layout.
For example, if you want to have more granular control and break the overall page grid into subgrids, see our user guide on Containers.
If you want to display multiple containers on one page by putting them into the same screen space, and letting the user switch between them, see our user guide on Tabs.